least effective sterilizer autoclave heat chemical|steam sterilization system : manufacture the heat of a steam sterilizer. Many hospitals still use ethylene oxide but in much smaller volumes. In 1995, . property that makes EtO an effective sterilant also makes it a known carcinogen. These hazards are mitigated by . Chemical sterilization generally fell by the wayside when Charles Chamberland developed the autoclave in Você sabe como fazer a limpeza da autoclave? Este flyer foi desenvolvido para ajudar você com os passos básicos da limpeza da .
{plog:ftitle_list}
Therefore, cleaning instructions may differ from manual to manual. In the interest of providing a uniform, up-to-date cleaning methodology suitable for all steam sterilizers, the following .
Recognized minimum exposure periods for sterilization of wrapped healthcare supplies are 30 minutes at 121°C (250°F) in a gravity displacement sterilizer or 4 minutes at 132°C (270°F) in a prevacuum sterilizer (Table 7).
Chemical indicators usually are either heat-or chemical-sensitive inks that .the heat of a steam sterilizer. Many hospitals still use ethylene oxide but in much smaller volumes. In 1995, . property that makes EtO an effective sterilant also makes it a known carcinogen. These hazards are mitigated by . Chemical sterilization generally fell by the wayside when Charles Chamberland developed the autoclave in
Sterilization Cycle Verification. A sterilization process should be verified before it is put into use in healthcare settings. All steam, ETO, and other low-temperature sterilizers are tested with biological and chemical indicators upon installation, when the sterilizer is relocated, redesigned, after major repair and after a sterilization failure has occurred to ensure they are . There are four basic methods of sterilization. Heat and chemical are most commonly used in hospitals. Filtration and radiation are used primarily for industrial applications. The first installment of this two-part Fundamentals Of column will explore heat sterilization and some general issues common to all sterilizers. The second installment .Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like The amount of pressure necessary in a steam sterilizer set at 250 F is: A. 15- 17 lb B. 20- 22 Ib C. 22- 25 Ib D. 25- 27 Ib, Positive assurance that sterilization conditions have been achieved can only be obtained through: A. Biological control test B. Heat- sensitive tape C. Color change monitor D. Mechanical . How do you use an autoclave? Once the chamber is sealed, all the air is removed from it either by a simple vacuum pump (in a design called pre-vacuum) or by pumping in steam to force the air out of the way (an alternative design called gravity displacement).Next, steam is pumped through the chamber at a higher pressure than normal atmospheric pressure so it .
Autoclaves, or steam sterilizers, are used to sterilize devices that are not heat-sensitive.A steam sterilizer uses time, psi (pressure), and 95-98% steam saturation to sterilize devices. Stainless steel surgical instruments can tolerate high temperature steam sterilization, while many endoscopes and other heat-sensitive semi-critical devices would be damaged. There are four basic methods of sterilization. Heat and chemical are most commonly used in hospitals. Filtration and radiation are used primarily for industrial applications. The first installment of this two-part Fundamentals Of column will explore heat sterilization and some general issues common to all sterilizers. The second installment .Dry heat can also be applied for relatively long periods of time (at least 2 hours) at temperatures up to 170 °C by using a dry-heat sterilizer, such as an oven. However, moist-heat sterilization is typically the more effective protocol because it penetrates cells better than dry heat does.
is the walmart assessment test hard

Many of the items used in modern healthcare facilities can be steam sterilized, but fiberoptic endoscopes, plastic devices, and electronics-laden items may demand a different technique. Chemical sterilization, which may be compatible with these types of devices, has gained popularity since the 1950s. B. atrophaeus spores should be used to monitor the sterilization process for dry heat because they are more resistant to dry heat than are G. stearothermophilus spores. The primary lethal process is considered to be oxidation of cell constituents. There are two types of dry-heat sterilizers: the static-air type and the forced-air type.
There is a chemical vapor dry-heat sterilizer that may sterilize in 20 min at 132 °C. Its effects on polymers, however, is unknown. It does sterilize metal instruments without dulling, rusting, or corrosion, as steam sterilization may, and it is much faster than standard dry-heat sterilization with just heated air. 4.2.2. Ethylene oxide .
Heat sterilization failure results when direct contact between the sterilizing agent (e.g., steam, dry heat, or hot chemical vapors) and all surfaces of the items being processed does not occur for the appropriate length of time. . Biologically monitor every sterilizer at least once a week. Be sure to keep accurate records on all monitoring . Preparation: Items are cleaned and arranged in a manner that allows for optimal air circulation. Sterilization Cycle: The sterilizer is heated to the desired temperature, typically ranging from 160°C (320°F) to 180°C (356°F), and maintained for a specific period, often ranging from 30 minutes to over two hours, depending on the sterilization parameters and the items' thermal . High temperatures are needed for effective sterilization. Autoclaves are commonly operated at 121° Celsius. Some autoclaves can run cycles at even higher temperatures, like 132°C and 135°C . Dry heat method requires a higher temperature and longer contact time. It is less effective than moist heat (autoclaving). Nevertheless, dry heat is preferable to moist heat for decontamination of anhydrous materials and closed containers because the moisture component of the steam used in an autoclave will not effectively penetrate anhydrous .
steam sterilization test pack
Explore the inner workings of autoclaves for effective sterilization. Learn about high temps, pressure, and steam in the autoclaving process. (858) 800-3900. 0. EN EN ES . Charles Chamberland is credited with inventing the autoclave in 1884. However, heat and pressure had been used for years for sterilization with prototype devices dating . Sterilization- physical and chemical methods. Dry Heat. Moist Heat. Radiation. Alcohols. Aldehydes. Oxidizing agents. Sterilization methods. . Moreover, it is a highly effective and most reliable process. There are two major methods of using heat in sterilization which are dry heat and moist heat. . Autoclave tips. Ozone. Ozone sterilizer . In general, each cycle will take between 60 to 90 minutes. The sterilization duration varies, but is typically around 30 minutes, and the remaining cycle time is split between heating up and cooling down the chamber. On what is an autoclave effective? The sterilization process kills bacteria, viruses and bacterial spores.
The CU Biological Laboratory Waste Management Disposal Policy & Procedure requires that if an autoclave is used for the sterilization of pathogenic cultures or “suspect” infectious materials, then a commercially available Bacillus stearothermophilus or Bacillus subtilis var. niger test strips must be used at least once every 90 days to .A chemical solution used to sterilize instruments by immersing them for at least 10 hours is . the minimum temperature that must be reached is. Biological indicator. Which of the following verifies that autoclave sterilization has occurred? Sterilant. Which of the following destroys bacterial spores? . Which of the following is the most .To be effective, the autoclave must reach and maintain a temperature of 121° C for at least 30 minutes by using saturated steam under at least 15 psi of pressure. Increased cycle time may be necessary depending upon the make-up and volume of the load. . Tape indicators are adhesive-backed paper tape with heat sensitive, chemical indicator .
Dried or baked materials on the instrument make the removal process more difficult and the disinfection or sterilization process less effective or ineffective. IB: 2.c. Perform either manual cleaning (i.e., using friction) or mechanical cleaning (e.g., with ultrasonic cleaners, washer-disinfector, washer-sterilizers). IB: 2.d.Steam sterilization is generally carried out at temperatures between 121°C (250°F) and 134°C (273°F), under 15–30 psi (1.0–2.0 bar) pressure, between 10 and 60 min, depending upon the material and the type of organism to be inactivated. Table 4.3 gives typical steam sterilization conditions. The lower the temperature, the longer the exposure time required for sterilization.
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Which of the following verifies that autoclave sterilization has occurred? biological indicator chemical indicator heat-sensitive tape Julian date, A surgical technologist just opened an instrument set that is wet inside after undergoing steam sterilization. Which of the following is the MOST likely reason for the .
Autoclave or steam sterilization is a moist heat sterilizing technique that has prominent applicability in laboratories, industries, and hospitals to purify different samples, equipment and glassware.It uses high-pressure steam to destroy bacterial cells and fungal spores.. It is one of the types of steam sterilizers that removes contaminants from the goods as a regular pressure . Autoclave sterilization is one of the most common methods that I have often seen various industries use to maintain safe and sterile environments. It is one of the most widely used cost-effective methods of sterilization and is a standard contamination control process in industries, such as healthcare, research labs, and certain manufacturing facilities.Generating Steam and Steam Quality. Steam is the autoclave’s sterilization agent. In our Sterilization Methods series, we explained the physics of steam and why steam sterilization is ideal for destroying microorganisms such as bacteria and spores. Part 1 of this post will explain how steam is generated for autoclaving purposes.
is the washington state knowledge test hard
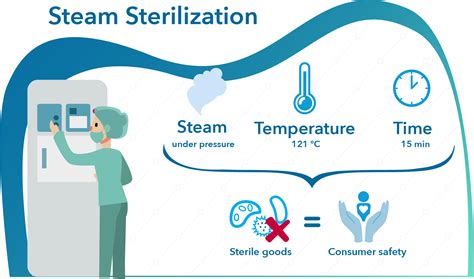
steam sterilization temperatures
steam sterilization system
decontamination vs sterilization
waste at its solid waste facility. 4.“Autoclaving,” means using a combination of heat, steam, pressure, and time to achieve sterile conditions. 5.“Biohazardous medical waste” is .
least effective sterilizer autoclave heat chemical|steam sterilization system